The Fulcrum of Commerce: How Digital Transformation and ERP are Reinventing the Warehouse Industry
2025-10-15 · By Anil Kancharla · 8 min read
❤️ 0 Likes · 👁️ 0 Views
 AI-generated image for illustration purposes only.
AI-generated image for illustration purposes only.
The Fulcrum of Commerce: How Digital Transformation and ERP are Reinventing the Warehouse Industry
 AI-generated image for illustration purposes only.
AI-generated image for illustration purposes only.
The Fulcrum of Commerce: How Digital Transformation and ERP are Reinventing the Warehouse Industry
October 15, 2025 – The warehouse has always been the unsung hero of commerce. It's the silent, sprawling space that holds the products that power our lives, from the essentials on our grocery shelves to the components that build our cars. For decades, its role was simple: to store goods. Today, that role has been radically transformed. The modern warehouse is no longer a static storage facility; it is the dynamic, high-velocity heart of the entire supply chain.
As we stand in the mid-2020s, the warehousing and storage industry is under immense pressure. It's at the epicenter of the e-commerce explosion, facing unprecedented demands for speed and accuracy. It's grappling with a persistent labor crisis, the complexities of omnichannel retail, and a new generation of customers who expect flawless, instantaneous fulfillment. The old model of manual processes and paper-based tracking is simply not equipped for this new reality.
The only way forward is through a profound operational reinvention, driven by digital transformation. And the foundational technology, the central nervous system that connects every pallet, every picker, and every process, is a modern Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system.
This in-depth blog post will explore the complex world of the modern warehouse, uncover the immense opportunities of its digital evolution, and provide a comparative analysis of leading ERP solutions that are helping warehouses become the strategic assets of the future.
More Than Just Four Walls: The Modern Fulfillment Center
To understand the impact of digital transformation, we must first appreciate the evolution of the warehouse. It is no longer a place where goods come to rest; it's a place where they are in constant motion. The core processes have been supercharged by the demands of modern commerce:
- Receiving: Goods arrive from suppliers. This now involves rapid unloading, quality checks, and scanning every item into a management system to make it instantly available for sale.
- Put-Away: Items are intelligently moved from the receiving dock to an optimal storage location. This is no longer about finding any empty shelf; it's about strategic placement to make future picking more efficient.
- Storage: Goods are stored in a way that maximizes space and ensures accessibility.
- Picking: This is the most labor-intensive process, where workers retrieve items from shelves to fulfill customer orders. The shift from picking full pallets for retail stores to picking single items for e-commerce orders has made this exponentially more complex.
- Packing: Picked items are consolidated, checked for accuracy, and packed into appropriate shipping containers with the correct documentation.
- Shipping: Packed orders are sorted by carrier, loaded onto trucks, and sent on their way to the end customer.
The Tipping Point: Challenges Forcing a Digital Shift in 2025
The pressures on today's warehouses are forcing a move away from manual methods toward intelligent, technology-driven operations.
- The E-commerce Explosion: The sheer volume and velocity of e-commerce have broken traditional warehousing models. The need to pick and ship thousands of small, multi-item orders every day with near-perfect accuracy and two-day (or faster) delivery windows is the new standard.
- The Labor Crisis: Warehousing is a physically demanding job, and the industry faces a chronic shortage of skilled labor. This drives up wages, increases turnover, and makes it difficult to scale operations during peak seasons.
- The Demand for Total Visibility: Customers—both B2B and B2C—now expect real-time visibility. They want to know if an item is in stock before they order it, and they want to track their package from the moment they click "buy" until it arrives at their door.
- Inventory and Returns Complexity (Reverse Logistics): Managing tens of thousands of unique SKUs is a challenge in itself. Adding in the complexity of omnichannel fulfillment (fulfilling online orders from a distribution center, a retail store, or even a third-party partner) and the high volume of e-commerce returns creates a logistical puzzle of epic proportions.
The Digital Upgrade: Key Transformation Opportunities
Digital transformation is providing a powerful toolkit to solve these challenges, turning the warehouse into a "smart," connected, and highly efficient environment.
-
The Warehouse Management System (WMS): The Operational Brain A WMS is the software that directs, controls, and optimizes all activities within the four walls of the warehouse. It manages inventory in real-time and directs staff on the most efficient way to perform tasks. Key capabilities include:
- Optimized Picking Strategies: Directing workers on the most efficient path to pick multiple orders at once (batch picking, zone picking, wave picking).
- Slotting Optimization: Using data to determine the best physical location for every SKU based on its velocity, ensuring that fast-moving items are in the most accessible locations.
- Real-Time Task Management: Digitally assigning tasks to workers via mobile scanners and tracking completion in real-time.
-
Automation and Robotics: The New Workforce Automation is key to solving the labor crisis and boosting productivity. This technology exists on a spectrum:
- Conveyors and Sortation Systems: Automated systems for moving goods through the warehouse.
- Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs): "Goods-to-person" robots that bring shelves of products directly to a stationary human picker, eliminating wasted travel time.
- Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS): High-density robotic systems that can store and retrieve totes or pallets automatically, ideal for maximizing storage space.
-
Data Capture and IoT Accurate, real-time data is the fuel for the smart warehouse. This is enabled by:
- Barcodes and RFID: Allowing for instantaneous identification and tracking of every item, pallet, and location with a simple scan.
- IoT Sensors: Placed on equipment like forklifts to monitor performance and enable predictive maintenance, or in the facility to monitor temperature and humidity for sensitive goods.
The Central Command Center: ERP as the Unifying Force
A powerful WMS can optimize the warehouse, but it can't run the business. The warehouse is part of a larger ecosystem that includes sales, purchasing, customer service, and finance. The Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system is the platform that unifies the warehouse with the entire enterprise.
While a WMS knows what is in the warehouse and where it is, the ERP knows why it's there, how much it cost, and where it needs to go next.
Core Benefits of an Integrated ERP and WMS:
- A Single Source of Truth for Inventory: The ERP holds the master record of inventory for the entire company. When the WMS receives a new shipment, it updates the ERP in real-time, making that inventory instantly visible and available for sale on the e-commerce site. This eliminates the risk of selling out-of-stock items.
- Seamless Order-to-Cash Cycle: When a customer places an order online, it flows directly into the ERP. The ERP validates the order and sends a fulfillment request to the WMS. The WMS directs the picking and packing. Once the order is shipped, the WMS notifies the ERP, which then automatically generates an invoice and triggers the accounting process.
- Intelligent Procurement and Demand Planning: The ERP analyzes sales data from all channels to forecast future demand. This allows the procurement team to make smarter purchasing decisions, ensuring the warehouse is stocked with the right products at the right time, preventing both stockouts and excess inventory.
- Holistic Business Intelligence: By integrating data from the warehouse (like labor costs per order and pick times) with financial and sales data in the ERP, managers can get a true, holistic view of profitability and operational efficiency.
Choosing Your System: A Look at Leading ERPs with WMS Capabilities
The ERP market offers powerful solutions that either include a native WMS module or integrate seamlessly with best-of-breed WMS platforms.
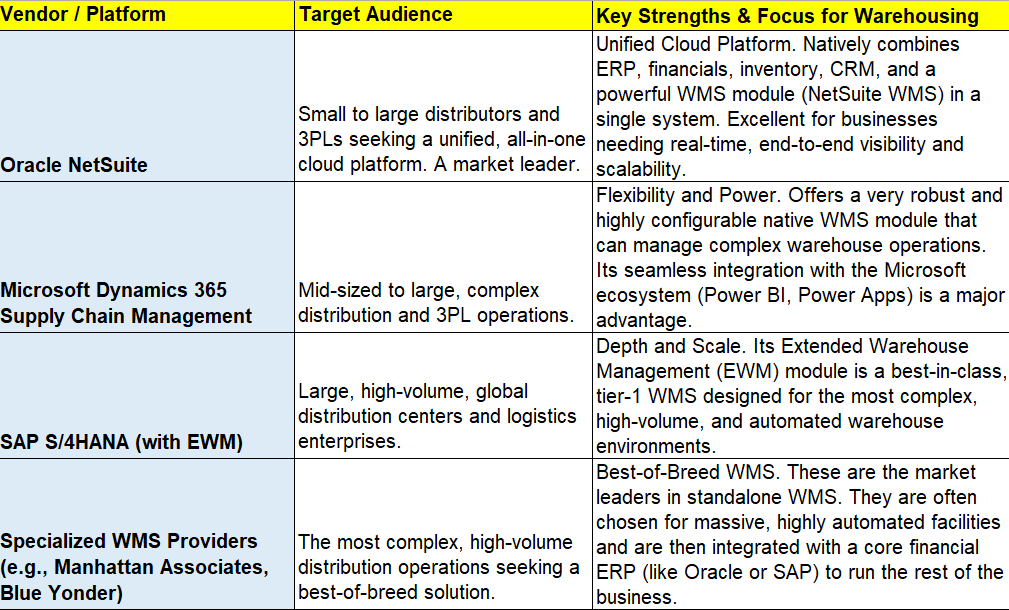
Building the Warehouse of the Future
The warehouse is no longer a cost center to be minimized; it is a strategic asset and a critical component of the customer experience. The companies that will win in the future of commerce are those that can fulfill orders faster, more accurately, and more efficiently than their competitors. This level of performance is not possible with outdated systems.
By embracing digital transformation and building their operations on the solid foundation of an integrated ERP and WMS, businesses can unlock the full potential of their warehouse, turning it into a powerful engine for growth and customer satisfaction.
💌 Enjoyed this article?
If you found this post valuable, subscribe to my newsletter for more insights on digital transformation, AI, and business innovation.
👉 Subscribe to the newsletterOr let’s connect on LinkedIn — I share weekly content that’s practical for CIOs, CFOs, and transformation leaders.
🔗 Connect with me on LinkedIn